Keyword
Frequantly asked Question


Show All






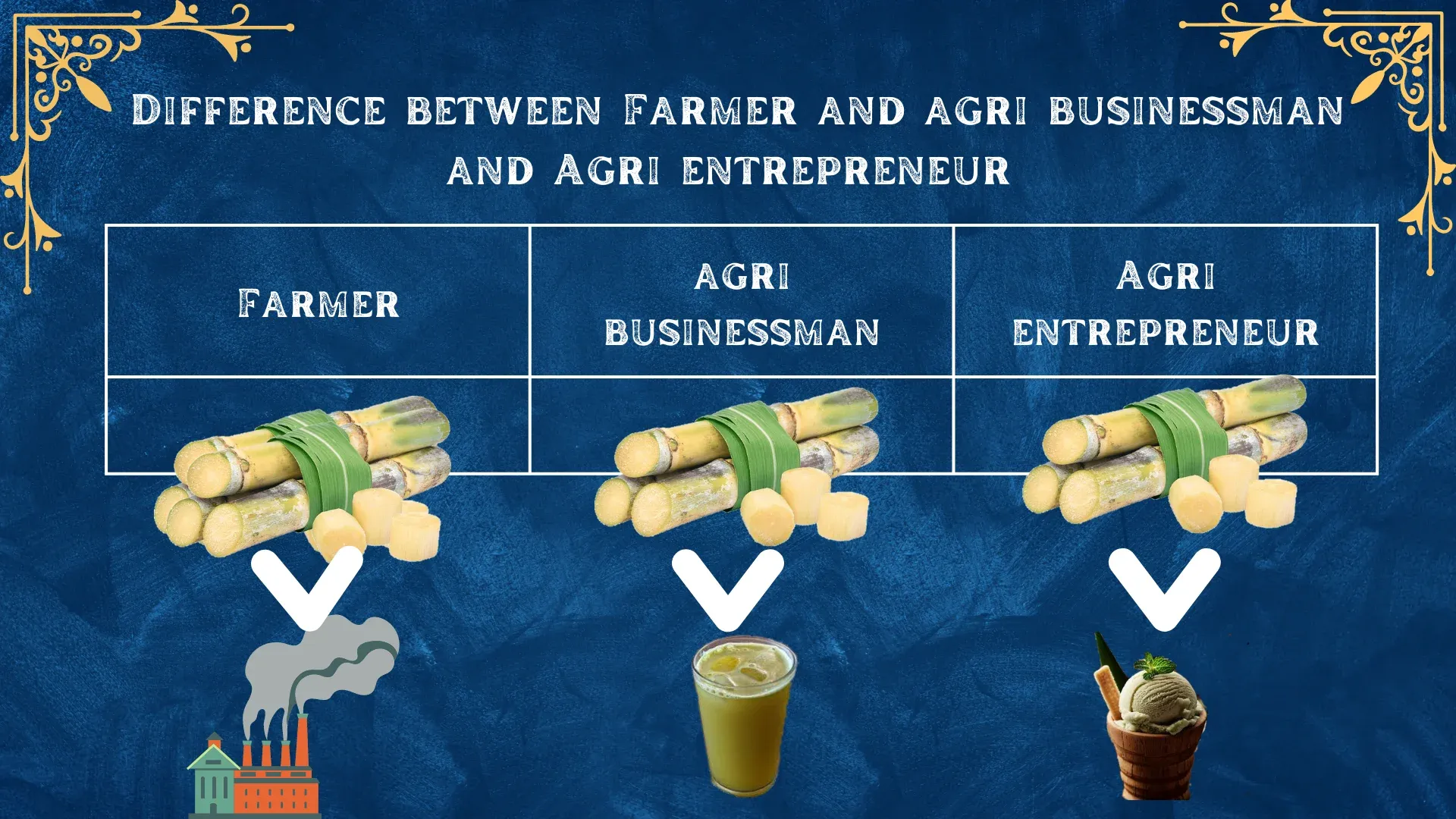
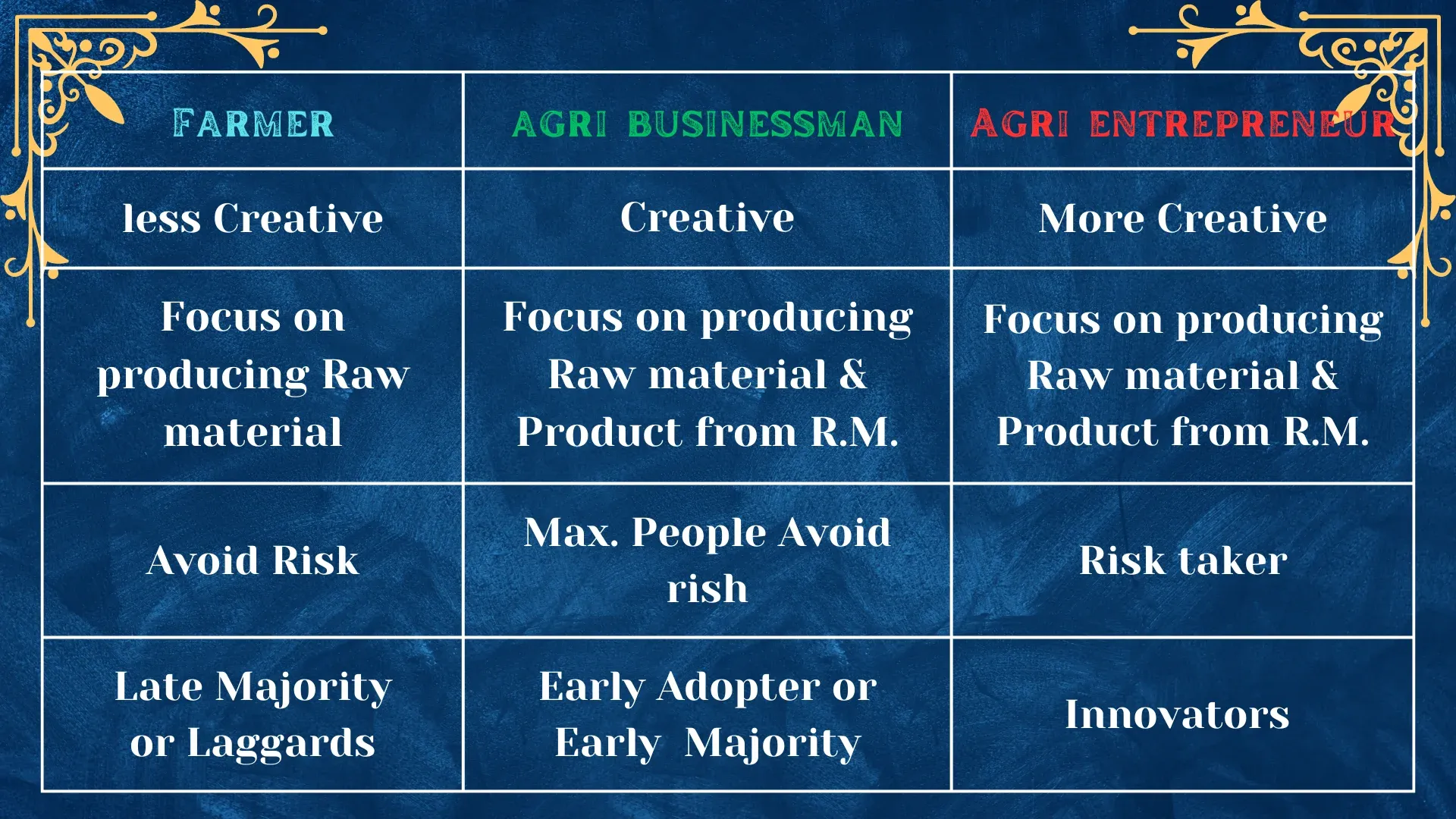

What is Agri-Entrepreneurship?
Summary
The term "Agri entrepreneurship" or "Agripreneurship" refers to entrepreneurial activities within the agricultural sector, encompassing the adoption of innovative methods, processes, and techniques aimed at improving agricultural output and economic returns. Sustainable agriculture, as described by Bahal (2008), involves a comprehensive approach to farming that emphasizes the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors. In simpler terms, sustainable agriculture entails farming practices designed to meet the fundamental needs of farmers while considering long-term viability and ecological impact..
In Hindi: कृषि-उद्यमिता क्या है?
कृषि-उद्यमिता कृषि के क्षेत्र में एक प्रकार की उद्यमिता है।
या
कृषि उद्यमिता को आम तौर पर स्थायी समुदाय-उन्मुख सीधे कृषि विपणन के रूप में परिभाषित किया जाता है
सतत कृषि, खेती के लिए एक समग्र, प्रणाली उन्मुख दृष्टिकोण है और यह प्रक्रिया सामाजिक, आर्थिक और पर्यावरण के अंतर्संबंधों पर केंद्रित है। (बहाल। 2008),
सामान्य भाषा में, टिकाऊ कृषि का अर्थ है खेती की एक प्रणाली जो किसानों की बुनियादी जरूरत को पूरा करने के लिए शुरू की जाती हैं।
Agri-entrepreneurship is a type of entrepreneurship in the field of agriculture.
Sustainable agriculture is a holistic, system-oriented approach to farming that focuses on interrelationships of social, economic & environmental in the process. (Bahal. 2008),
In layman's language, sustainable agriculture means a system of farming Started to fulfil the basic needs of farmers.
Why Agri-Entrepreneurship is Important for Agriculture Development?
Summary
The importance of agri-entrepreneurship in agricultural development is underscored by the abundance of commodities available in various areas of agriculture, which could otherwise go to waste. Agri-entrepreneurs play a crucial role in utilizing these commodities efficiently. Several factors contribute to the significance of agri-entrepreneurship, including the increasing demand for organic and high-quality food domestically and internationally. Additionally, there is a competitive advantage in various primary production activities within agriculture, such as tropical fruits and vegetables, livestock rearing, aquaculture, and rain-fed farming. Private enterprises are increasingly interested in agri-business due to evolving consumer preferences and changes in the retail landscape. Moreover, promoting agri-entrepreneurship can help reduce malnutrition and provide opportunities for surplus labor to start their own agricultural businesses..
In Hindi: कृषि विकास के लिए कृषि-उद्यमिता क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है?
प्रश्न - कृषि विकास के लिए कृषि व्यवसाय क्यों
महत्वपूर्ण है?
उत्तर - क्योंकि कृषि में कई
ऐसे क्षेत्र और उप-क्षेत्र हैं जहां बड़ी संख्या में वस्तुएं उपलब्ध हैं,
या बर्बाद हो जाती हैं, लेकिन कृषि उद्यमिता इन वस्तुओं का उपयोग कर सकती
है और इन के सहारे फल-फूल सकती है।
कुछ अन्य कारक निम्नलिखित हैं
(ए)
भारत के साथ-साथ विदेशों में भी जैविक / गुणवत्ता वाले भोजन की बढ़ती
मांग।
(बी) कृषि में कई प्राथमिक उत्पादन गतिविधियों जैसे
उष्णकटिबंधीय फल और सब्जियां, पशुधन पालन, जलीय कृषि, वर्षा आधारित खेती
आदि के लिए प्रतिस्पर्धात्मक लाभ।
(सी) उपभोक्ता मांग और खुदरा
क्रांति को बदलने के सभी स्तरों पर कृषि व्यवसाय में प्रवेश करने के लिए
निजी क्षेत्र की इच्छा।
(डी) कुपोषण को कम करने के लिए,
(ई)
अधिशेष श्रम को अपने स्वयं के कृषि व्यवसाय शुरू करने में सहायता करना।
What are Opportunities for Agri-Entrepreneurs?
Summary
Your_text_is_here.
In Hindi: कृषि-उद्यमियों के लिए क्या अवसर हैं?
1. विविधता:
कृषि में विविधीकरण का तात्पर्य पारंपरिक रूप से उगाई जाने वाली कम लाभकारी फसलों के स्थान पर अधिक लाभकारी फसलों जैसे तिलहन, दलहन, चारा फसलों, बागवानी, औषधीय और सुगंधित पौधों, फूलों की खेती आदि कराने से है। विविधीकरण से रोजगार के अवसर, संसाधनों का इष्टतम उपयोग और लाभप्रदता बढ़ती है।
2. जैविक खेती:
जैविक खेती कृषि आधारित उद्यमियों को व्यवसाय के अवसर प्रदान करती है। जैविक खेती के तहत क्षेत्र बढ़ रहा है लेकिन जैविक उत्पादों की मांग को पूरा करने में असमर्थ है। जैविक खेती का महत्व बहुत तेजी से बढ़ रहा है, खासकर अंतरराष्ट्रीय बाजार में।
3. खाद्य संरक्षण, प्रसंस्करण और पैकेजिंग:
प्रोसेस्ड फूड की मांग तेजी से बढ़ रही है। फिर भी, भारत में भण्डारण की कमी वा परिवहन और खाद्य प्रसंस्करण सुविधाओं की कमी के कारण कृषि उपज की काफी मात्रा बर्बाद हो जाती है। । इसलिए कृषि-उद्यमी उचित प्रबंधन और विपणन पहलों के साथ मूल्यवर्धन कर सकते हैं।
4. कृषि-इनपुट का उत्पादन:
किसान उद्यमशीलता की गतिविधियां जैसे की बीज, जैविक खाद और कीटनाशकों का उत्पाद शुरू कर सकते हैं।
1. Diversification:
2. Organic farming:
3. Food Preservation, Processing and Packaging:
4. Production of agro-inputs:
What are the Constrain/Problems Perceived by Agri Entrepreneur?
Summary
The given paragraph outlines various constraints across socio-personal, technological, economic, and communicational aspects that hinder the adoption of innovations in rural areas.
A. Socio-personal constraints highlight issues such as lack of consumer awareness and motivation, insufficient knowledge about innovations, low education levels, and poor investment due to inadequate savings.
B. Technological constraints encompass challenges such as the absence of regular and effective training, limited access to inputs, innovations being perceived as beyond the reach of common people, and inadequate scientific processing, storage, and marketing facilities.
C. Economic constraints involve factors like the lack of finance, unavailable loan facilities for purchasing inputs, high input costs, and the difficulty and expense of maintaining or managing new practices.
D. Communicational constraints encompass inadequate access to training programs, poor infrastructure especially concerning transport and communication, weak relationships with extension agencies, and limited social mobility for rural women.
In essence, these constraints collectively impede the uptake of innovations in rural areas, necessitating targeted interventions to address these multifaceted challenges..
In Hindi: कृषि उद्यमी द्वारा अनुभव की जाने वाली बाधाएं/समस्याएं क्या हैं?
A. सामाजिक-व्यक्तिगत बाधाएं
- उपभोक्ता जागरूकता और प्रेरणा का अभाव।
- नवाचारों के बारे में प्रासंगिक ज्ञान का अभाव।
- शिक्षा का निम्न स्तर।
- खराब बचत के कारण खराब निवेश।
B. तकनीकी बाधाएँ
- नियमित और प्रभावी प्रशिक्षण का अभाव।
- आदानों की खराब पहुंच।
- दिखाई गई तकनीक आम लोगों की पहुंच से बाहर है।
- वैज्ञानिक प्रसंस्करण, भंडारण और विपणन सुविधाओं का अभाव।
C. Economic constraints
- वित्त की कमी।
- आदानों की खरीद के लिए ऋण सुविधाओं की अनुपलब्धता
- आदानों की उच्च लागत।
- नई तकनीकों का कठिन और महंगा रखरखाव/प्रबंधन।
D. Communicational constraints
- प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रमों तक अपर्याप्त पहुंच।
- खराब आधारभूत संरचना, विशेष रूप से परिवहन और संचार सुविधाएं।
- विस्तार एजेंसियों के साथ खराब संबंध।
- ग्रामीण महिलाओं की कम सामाजिक गतिशीलता।
A. Socio-personal constraints
B. Technological constraints
C. Economic constraints
D. Communicational constraints
Related Posts
Reference
